position俗称定位,主要取值及作用如下:
|
static |
默认值。没有定位,出现在正常文档流中 |
|
absolute |
绝对定位,相对于position为absolute、relative、fixed的第一个父元素进行定位 |
|
relative |
相对定位,相对于其正常位置进行定位 |
|
fixed |
绝对定位,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位 |
Position本不复杂,混淆应用比较难理解,主要规则如下:
除 static属性值之外,其他值都会使元素脱离文档流(float也会导致元素脱离文档流)。
1) Absolute的参考点为最近可作为参考点的父元素(position为absolute、relative、fixed的元素)、
fixed的参考点浏览器窗口、relative的参考点为元素正常位置。
2) 元素本身值为inherit时
a) 当父级元素的Width和height值为数值时,元素继承父级元素的完整高度,并以最近参考点作为参考。
.wrap{ position: relative; width: 500px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; } .cont{ background: gray; width: 150px; overflow: hidden; } .txt{ background: yellow; width: 230px; height: inherit; } .banner{ background: pink; width: 50%; height: inherit; } .txt-cont{ position: absolute; background: darkblue; width: inherit; color: white; }
<div class="wrap"> <div class="cont"> cont <div class="txt"> txtxtxt <div class="txt-cont"> txt-cont </div> </div> <div class="banner"> banner </div> </div> </div>
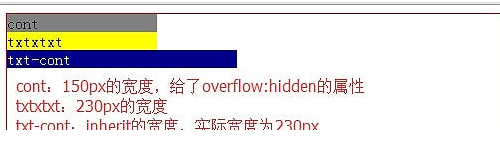
b) 当父级元素的Width和height值为百分比时,以参考点元素的宽、高* 百分比来计算。
.wrap{ position: relative; width: 500px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; } .cont{ background: gray; width: 150px; overflow: hidden; } .txt{ background: yellow; width: 50%; height: inherit; } .banner{ background: pink; width: 50%; height: inherit; } .txt-cont{ position: absolute; background: darkblue; width: inherit; color: white; }
<div class="wrap"> <div class="cont"> cont <div class="txt"> txt <div class="txt-cont"> txt-cont </div> </div> <div class="banner"> banner </div> </div> </div>

3) 元素本身为百分比时(50%)
此种情况下,无论父级元素的width和height是数值,还是百分比都不会造成对元素自身的影响,
元素自身还是会以参考进行相应的计算。
.wrap{ position: relative; width: 500px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; } .cont{ background: gray; width: 150px; overflow: hidden; } .txt{ background: yellow; width: 50%; height: inherit; } .banner{ background: pink; width: 50%; height: inherit; } .txt-cont{ position: absolute; background: darkblue; width: 100%; color: white; }
<div class="wrap"> <div class="cont"> cont <div class="txt"> txt <div class="txt-cont"> txt-cont </div> </div> <div class="banner"> banner </div> </div> </div>

Fixed和absolute属性后的默认位置都是在原地,只是紧跟后面折正常文档流元素会顶上来,
被定位元素盖住。
z-index的详细介绍见后面章节,此处只指出position除static值外都会创建层叠上下文
(z-index不为auto的时候)。
1) z-index为数值时,会创建层叠上下文,子元素层叠顺序以此做为参考。
2) z-index为auto时,不会创建层叠上下文,层叠顺序与z-index:0一致。

【 微信扫一扫 】